Taking Probiotics With Antibiotics
Antibiotics have transformed modern medicine by preventing and curing bacterial infections, resulting in bacterial infections being no longer the most common cause of death in the modern world1. However, it is now recognised that antibiotics disrupt our gut microbiome2,21 which has led to growing interest in probiotics being taken alongside antibiotics.
The good news is that evidence suggests taking probiotics alongside antibiotics may help to reduce adverse effects on the composition of the gut microbiome19. Read on to find out more about the best probiotics for antibiotics.
In this article we will look at the following:
- Which are the best probiotics to take alongside antibiotics?
- Antibiotics and gut health
- Why take a probiotic with an antibiotic?
- Can I take probiotics with antibiotics?
- Probiotics for children taking antibiotics
- When should I take probiotics when taking antibiotics?
- Should you take probiotics after antibiotics?
- Best probiotics for long-term antibiotic use?
- Do probiotics disturb antibiotic functioning?
- Important tips for supporting general health whilst on antibiotics
- Key takeaways: probiotics and antibiotics
Which are the best probiotics to take alongside antibiotics?
A question we often get asked is, which are the best probiotics with antibiotics to support antibiotic diarrhoea? It seems that this is the most commonly experienced side effect when taking this type of medication and can lead to a discontinuation of treatment.
In clinical trials involving individuals undergoing antibiotic treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection, participants were given Lactobacillus acidophilus Rosell-52, Lactobacillus rhamnosus Rosell-11 and Bifidobacterium lactis Lafti B94 alongside antibiotics. All three strains were proven to survive alongside the medication, enhance the efficacy of treatment and reduce side effects like diarrhoea, loss of appetite and pain11,12.
The recommended use for a supplement containing this probiotic combination is as follows:
- Take one capsule daily with breakfast, at the same time as your antibiotic medication.
- Take daily until the antibiotic course is finished, and ideally for one week after.
- Continue until the pack is completed and add a second pack if the antibiotic treatment lasts more than one week.
Those taking antibiotics for a vaginal health issue might also like to consider taking probiotic strains which are well researched for intimate health, such as Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14® and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1®. These strains are often used alongside antibiotics for vaginal infections but are best taken 2 hours away from the medication.
Health professionals can read more detail about these strains in the Probiotics Database: Lactobacillus reuteri RC-14® and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1®.
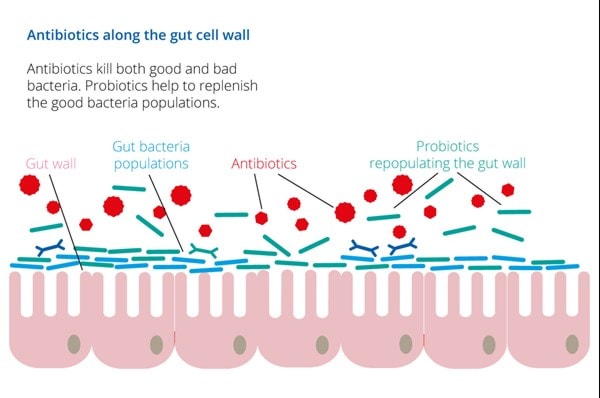
Antibiotics and gut health
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of trillions of microbes that live together in harmony in our gastrointestinal tract. These microbes have far reaching effects on human health, enhancing digestion, immunity, skin health and energy3,4,5. A balance is required between beneficial microbes and more harmful microbes that naturally colonise the gut. This balance can be disturbed by various lifestyle factors including low-fibre diet, travel and infection, among others.
So, what happens to our gut microbiome when we take an antibiotic? Unfortunately, taking antibiotics can be detrimental to our gut health. New research has found that the effects of antibiotics are detectable in the gut microbiome several years after use22. This 2025 study involving more than 2500 adults also found the effect of antibiotics can be “additive”, reprting that the more an antibiotic medication is used, the stronger the impact on the gut microbiome. Whilst effective in killing bad bacteria, antibiotics are essentially non-selective and can also deplete the beneficial bacteria residing in the gut. This is thought to contribute to the development of diarrhoea, constipation and/or vaginal thrush when taking an antibiotic. In certain cases, this disruption to our gut microbiome can result in an overgrowth of unwanted, pathogenic bacteria such as Clostridium difficile.
Of course, for active infection, the benefits of taking antibiotics far outweigh the associated negatives. Taking a probiotic alongside an antibiotic can help to minimise digestive upset that occurs as a result of the disruption to our gut microbiome, otherwise known as dysbiosis.
People taking antibiotics may experience6:
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Indigestion
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue, feeling low on energy or ‘wiped out’
- Antibiotic-associated diarrhoea
Why take a probiotic with an antibiotic?
Taking probiotics whilst taking antibiotics may help maintain gut microbiome health during antibiotic therapy. Replenishing the gut with beneficial bacteria helps to rebalance the gut microbiome and reduce the risk of developing common side effects of antibiotics. The NHS has recognised the beneficial effects of probiotic supplementation7. When prescribed antibiotics, many individuals now choose to supplement their natural bacteria with a probiotic supplement. Your local pharmacist may even recommend probiotics when dispensing your antibiotic presciption.
Antibiotic-associated diarrhoea (ADD) is one of the most common side effects of antibiotics, with a prevalence of between 5 to 35%, depending on the type of antibiotic8 taken. A meta-analysis of 23 studies from the highly esteemed Cochrane Collaboration carried out in 2012 (focusing on contrasting and combining results from multiple studies) found that probiotics can reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated side effects by 64%. One particular form of AAD is Clostridium difficile infection, which manifests as chronic diarrhoea and in severe cases, colitis. This is of particular concern in the elderly and can sometimes be fatal. Based on a systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 randomized controlled trials including 4213 patients, evidence suggests that probiotics are both safe and effective in helping to support the health of the gut microbiome and reducing digestive upset related to Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea10
A meta-analysis, conducted by the University of Toronto9, reviewed 16 separate studies encompassing a total of 3,403 patients undergoing antibiotic treatment. The results showed that patients supplemented with probiotics during antibiotic treatment had a significantly reduced risk of developing antibiotic-associated diarrhoea or C. difficile infection.

Can I take probiotics with antibiotics?
Yes. Extensive clinical research suggests the best probiotic to take with antibiotics are particular strains that can be taken alongside antibiotics, rather than separately. These particular strains are Lactobacillus acidophilus Rosell-52, Lactobacillus rhamnosus Rosell-11 and Bifidobacterium lactis Lafti B94 which we have already mentioned. The combination of these strains can be taken at exactly the same time as antibiotic medication, which is not the case for most other probiotic supplements.
Taking other probiotic strains with antibiotics isn’t necessarily bad, but some may not survive alongside the medication. However, rest assured, antibiotics will still work effectively. For best results we always recommend chossing probiotic strains that have been studied for your specific health needs.
Taking well-studied strains that have been shown to survive when taken at the same time as the antibiotic medication is particularly useful alongside intravenous (IV) antibiotics which may be constantly administered on a drip. It is a good idea to take probiotics during and after courses of antibiotics. We discuss more about taking probiotics after antibiotics later in this article.
Probiotics for children taking antibiotics
Many parents first start giving probiotic supplements to their children when they are given a course of antibiotics, as this type of medication can sometimes cause tummy upsets. Children aged four years and above are fine to take the above mentioned strains, Lactobacillus acidophilus Rosell-52, Lactobacillus rhamnosus Rosell-11 and Bifidobacterium lactis Lafti B94, as they have also been clinically trialled in children. It can be easier to use these strains , as there's no need to give them at a different time to the antibiotics. However, if their child is already taking a probiotic supplement especially formulated for children’s gut health, parents can opt to continue giving this with food a couple of hours away from the medication.
When should I take probiotics when taking antibiotics?
Generally, with a few exceptions aside, it is best to take probiotic supplements in the morning with breakfast. If you are taking a probiotic containing the strains Lactobacillus acidophilus Rosell-52, Lactobacillus rhamnosus Rosell-11 and Bifidobacterium lactis Lafti B94, you would still be able to follow this recommendation alongside antibiotics and take both with your breakfast.
However, if you are taking different strains, such as Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM®, Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07® or Bifidobacterium lactis Bl-04®, it is best to leave a 2 hour gap between antibiotics and taking the probiotic supplement. So, if you have been instructed by your doctor to take your antibiotics with breakfast, you would take the medication first in this instance and leave a 2 hour gap before taking the other probiotics. Any alternative probiotic strains taken should also have research demonstrating their efficacy during antibiotic therapy.
Should you take probiotics after antibiotics?
Even if you have taken a probiotic designed to be taken alongside your antibiotic medication, it is always a sensible idea to take good daily probiotics after antibiotics for at least a month or so to replenish the gut microflora. Scientists are not really sure exactly how long it will take to rebuild the gut flora after antibiotics; it will depend on several different factors such as the individual gut microbiome, the length of the course, the strength of medication, diet and lifestyle etc. What are the best probiotics after antibiotics? Well, studies show taking a probiotic supplement that contains the strains Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07® after antibiotics may help to stabilise Lactobacillus populations in the gut13. The Lactobacillus genus of friendly bacteria helps to crowd out the bad guys and keep our gut environment healthy.
Best probiotics for long-term antibiotic use?
The best probiotics when taking antibiotics long term are ones which have shown to be helpful in reducing side effects when taken at the same time. If you need to take a longer course of antibiotics, you may wish to consider choosing a supplement that contains Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM®. A supplement that contains this particular strain has been demonstrated in a randomised controlled trial to minimise disturbance to the composition of the gut microbiome when taken alongside antibiotics14. This can be useful when antibiotics are being taken for longer than two weeks. However, it is recommended to take this probiotic strain 2 hours away from an antibiotic, rather than at the exact same time. To find out more about the research using this strain, health professionals can go to the Probiotics Database: Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM®
Do probiotics disturb antibiotic functioning?
There is no suggestion in current research that probiotics interfere with the action of antibiotics in any way. In fact, doctors and GPs are often now recommending probiotic supplements and probiotic foods, such as yoghurts or kefir, to be taken alongside a course of antibiotics.
The over-prescription of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance
The emergence of antibiotic resistance is a concerning public health issue. The World Health Organisation (WHO) published a report1, analysing data from 114 countries, and calling resistance to antibiotics a 'major global threat'. They state that simple, common infections thought to pose little threat today, could become killers again in the future, due in large part to antibiotic resistance. In light of this, steps must be taken to slow the progress of antibiotic resistance, and to change the way we use and prescribe antibiotics. Over-prescription and over-use of antibiotics are significant contributing factors to the development of antibiotic resistance15. The over-prescription of antibiotics is a pertinent issue in the UK, with up to 23% of antibiotic prescriptions being deemed “inappropriate” by the NHS16.
Failure to complete a full course of antibiotics is also believed to contribute to antibiotic resistance15. Probiotics are being used increasingly to help support digestion during antibiotic use which may enable patients to complete their medication. Health professionals might be interested to read more about the use of probiotics against antibiotic resistance.

Probiotics vs Antibiotics? You’re asking the wrong question.
The question of whether someone should be taking a probiotic or an antibiotic is commonly asked. The answer, in short, is that it isn't a question of either but instead, whether a probiotic should be taken in addition to, or alongside, an antibiotic. The answer to this question is, in most cases, yes!
There are some conditions where sufferers may prefer trying natural interventions first. Acne is a very common skin issue where antibiotics are often prescribed as a treatment by a general practitioner or dermatologist. In a 2011 literature review, it was determined that there is sufficient supportive evidence to suggest that gut microbes, and the health of the gastrointestinal tract itself, may be contributing factors in acne vulgaris3. You may like to read our FAQ about probiotics and skin health. However, this decision should always be made in line with a doctor’s consent.

Important tips for supporting general health whilst on antibiotics
- Eat fermented or prebiotic foods. These can help rebalance the gut microbiome and optimise gut health after a course of antibiotics.
- Avoid refined sugary foods, as these feed the harmful bacteria and yeasts which often overgrow due to antibiotic use.
- Avoid alcohol, even if not contraindicated with your course of antibiotics. Alcohol can also disrupt the gut microbiome and negatively impact immune function, which may hinder your body's efforts to fight infection.
- Ensure you complete your course of antibiotics. Unpleasant side effects can make it difficult to continue taking antibiotics but failing to complete the course can increase the risk of antibiotic resistance.
- Eat a healthy diet. Don't let the antibiotics do all the work - include a selection of immune-boosting foods containing Vitamin C and other antioxidants, including citrus fruits and green leafy vegetables.
Key takeaways: probiotics and antibiotics
- Antibiotics deplete the populations of friendly bacteria in the gut and may cause side effects such as diarrhoea, nausea, indigestion and low energy. It’s important to select probiotics to take with antibiotics, don’t wait until the course has finished.
- If taking Lactobacillus acidophilus Rosell-52, Lactobacillus rhamnosus Rosell-11 and Bifidobacterium lactis Lafti B94 then take them with breakfast. These strains can be taken at the same time as your antibiotic.
- If taking a different probiotic supplement, like Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07® or Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM® wait at least 2 hours after your antibiotics before taking probiotics.
- It is important to always follow the advice from your doctor, and always take and finish a course of antibiotics as prescribed. Taking probiotics alongside antibiotics may reduce digestive issues and enable you to finish a course, reducing the chances of antibiotic resistance.
- If you have already finished a course of antibiotics before being recommended a probiotic supplement, better late than never. For next time, you know you can take them during as well as after.
You may also wish to read At what time should I take probiotics?
References
- Achievements in Public Health, 1900-1999: Control of Infectious Diseases. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm4829a1.htm. Accessed April 16, 2020.
- Yoon MY, Yoon SS. Disruption of the gut ecosystem by antibiotics. Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(1):4-12. doi:10.3349/ymj.2018.59.1.4
- Bowe WP, Logan AC. Acne vulgaris, probiotics and the gut-brain-skin axis - Back to the future? Gut Pathog. 2011;3(1):1. doi:10.1186/1757-4749-3-1
- Zhang YJ, Li S, Gan RY, Zhou T, Xu DP, Li H Bin. Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):7493-7519. doi:10.3390/ijms16047493
- Kamada N, Seo SU, Chen GY, Núñez G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(5):321-335. doi:10.1038/nri3430
- Antibiotics - Side effects - NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/antibiotics/side-effects/. Accessed April 15, 2020.
- Probiotics - NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/probiotics/#diarrhoea. Accessed April 15, 2020.
- Mcfarland L V. Epidemiology, Risk Factors and Treatments for Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea Antibiotic complications Antibiotic-associated diarrhea Clostridium difficile Epidemiology Diarrhea, risk factors. 1998;98102:292-307. http://www.karger.com.
- Videlock EJ, Cremonini F. Meta-analysis: Probiotics in antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;35(12):1355-1369. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.05104.x
- Goldenberg JZ, Ma SSY, Saxton JD, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(5). doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006095.pub3
- Pattani, R. et al (2013) Probiotics for the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea and Clostridium difficile infection among hospitalized patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. Open Medicine. Published online ahead of print.
- Johnson-Henry KC, Mitchell DJ, Avitzur Y, Galindo-Mata E, Jones NL, Sherman PM. Probiotics reduce bacterial colonization and gastric inflammation in H. pylori-infected mice. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49(7-8):1095-1102. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000037794.02040.c2
- Cekin, A.H. et al. (2017). 'Use of probiotics as an adjuvant to sequential H. pylori eradication therapy: impact on eradication rates, treatment resistance,treatment-related side effects, and patient compliance'. Turk J Gastroenterol: 28: 3-11
- Forssten, S., et al., (2014). ‘Influence of a probiotic mixture on antibiotic induced microbiota disturbances’. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20(33):11878-85.
- Engelbrektson A, Korzenik JR, Pittler A, et al. Probiotics to minimize the disruption of faecal microbiota in healthy subjects undergoing antibiotic therapy. J Med Microbiol. 2009;58(5):663-670. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.47615-0
- Ventola CL. The antibiotic resistance crisis: causes and threats. P T J. 2015;40(4):277-283. doi:Article
- Up to 1 in 5 antibiotics may be prescribed inappropriately - NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/news/medication/1-5-antibiotics-may-be-prescribed-inappropriately/. Accessed April 16, 2020.
- Falagas ME, Kotsantis IK, Vouloumanou EK, Rafailidis PI. Antibiotics versus placebo in the treatment of women with uncomplicated cystitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Infect. 2009;58(2):91-102. doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2008.12.009
- Ranjan A (2022) The Use of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics as an Alternative to Antibiotics. In: Saha, T., Deb Adhikari, M., Tiwary, B.K. (eds) Alternatives to Antibiotics. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1854-4_18
- Fernández-Alonso, M., et al. (2022) Effect of adding probiotics to an antibiotic intervention on the human gut microbial diversity and composition: A systematic review. Journal of Medical Microbiology. doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.001625.
- Li, X., Brejnrod, A., Thorsen, J. et al. Differential responses of the gut microbiome and resistome to antibiotic exposures in infants and adults. Nat Commun 14, 8526 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-44289-6
- Aasmets O, Taba N, Krigul KL, Andreson R, , Org E. (2025). A hidden confounder for microbiome studies: medications used years before sample collection. mSystems 10:e00541 https://doi.org/10.1128/msystems.00541-25
Popular Articles
View all General Health articles-
General Health07 Jan 2025
-
General Health16 Nov 2023

